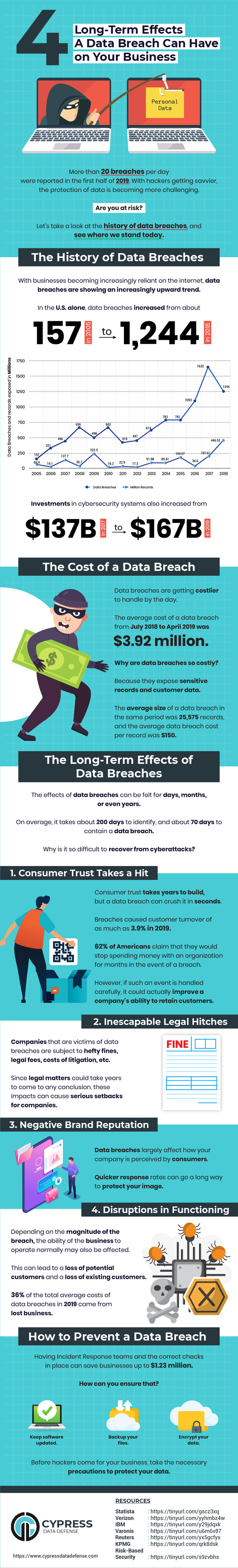
As more and more companies become victims of cybersecurity attacks, the wave of data loss and breaches is on the rise.
Cybersecurity research reveals that most companies have poor cybersecurity practices in place and have unprotected data, making them vulnerable to attacks.
Some of the most common cyberattacks include ransomware, malware, phishing, SQL Injection, XSS attacks, and insider threats.
How does a data breach occur?
A data breach starts when an attacker infiltrates an organization’s network. Once the attacker has access to your network or servers, they can steal your data by bypassing security remotely.
Most data breaches include credit card theft, fraud, or loss of sensitive information such as customer’s data including their name, age, contact details, addresses, banking information, etc. Some data breaches are even caused by human error.
For instance, if an employee attempts to access the company’s email via an unprotected Wi-Fi network, it’s possible for an attacker to hack their network and get access to their data. Such data breaches caused by human error are known as insider threats.
The long-term impact of a data breach is often devastating.
Ransomware alone cost businesses more than $8 billion per year in 2018. In addition to this, a data breach not only impacts a company’s revenue but also severely damages its brand reputation.
Here are some of the major long-term effects of a data breach on an organization:
Author Bio – Aaron Cure


After 10 years in the U.S. Army, I decided to switch my focus to developing security tools and performing secure code reviews, penetration testing, static source code analysis, and security research.
All opinions and facts are that of a third-party writer, not an official Feenta.com author. It’s an article written by a guest author. If you’d like to submit an article, go to our Write for Us page.